Turn your network into revenue with our digital marketing affiliate program, a straightforward, high-value way to earn by introducing mid-size and larger organisations to Seek Marketing Partners. If your contacts make marketing decisions and you want a professional, results-driven referral option without handling delivery yourself, this offer is for you.
Why Our Digital Marketing Affiliate Program Works
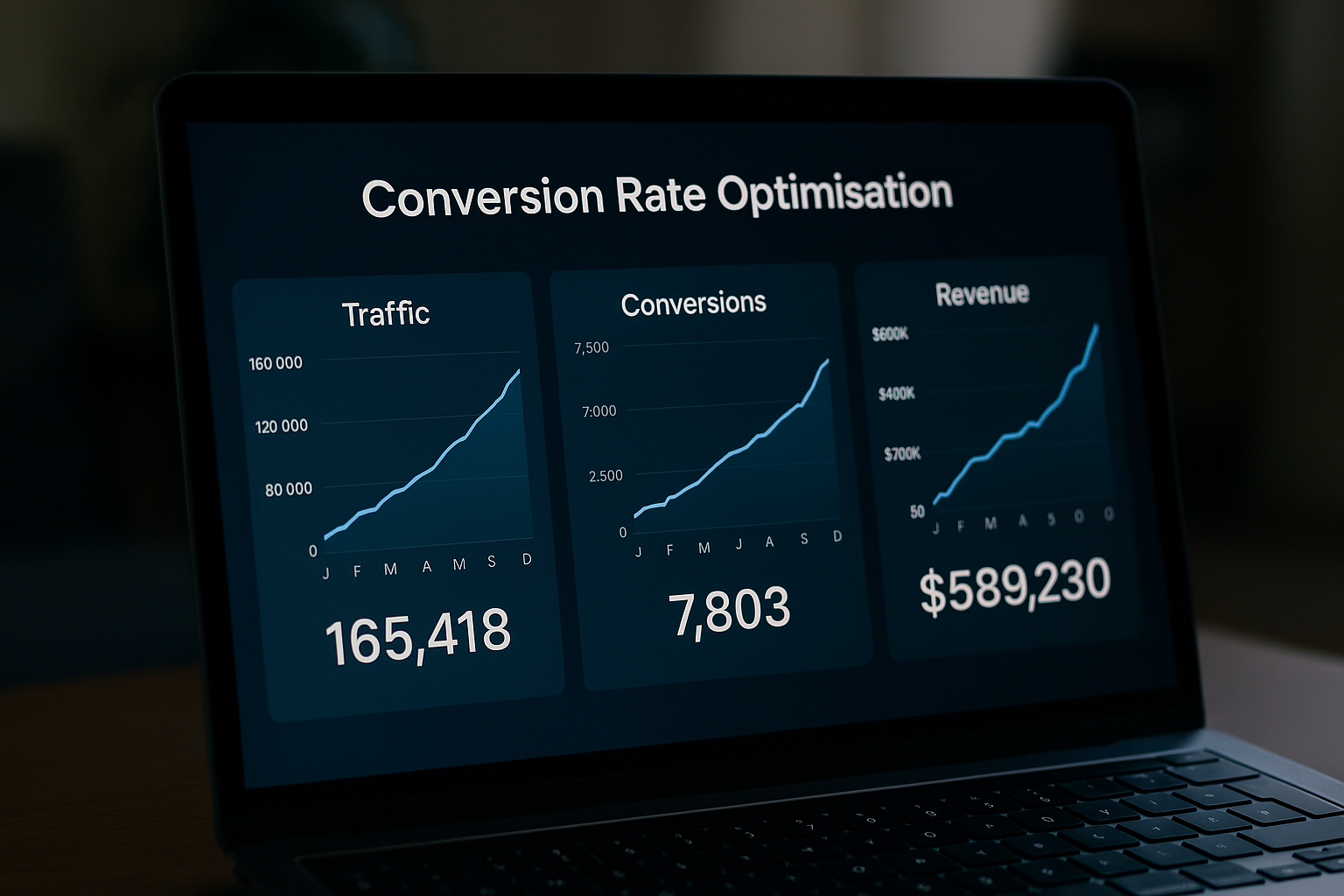
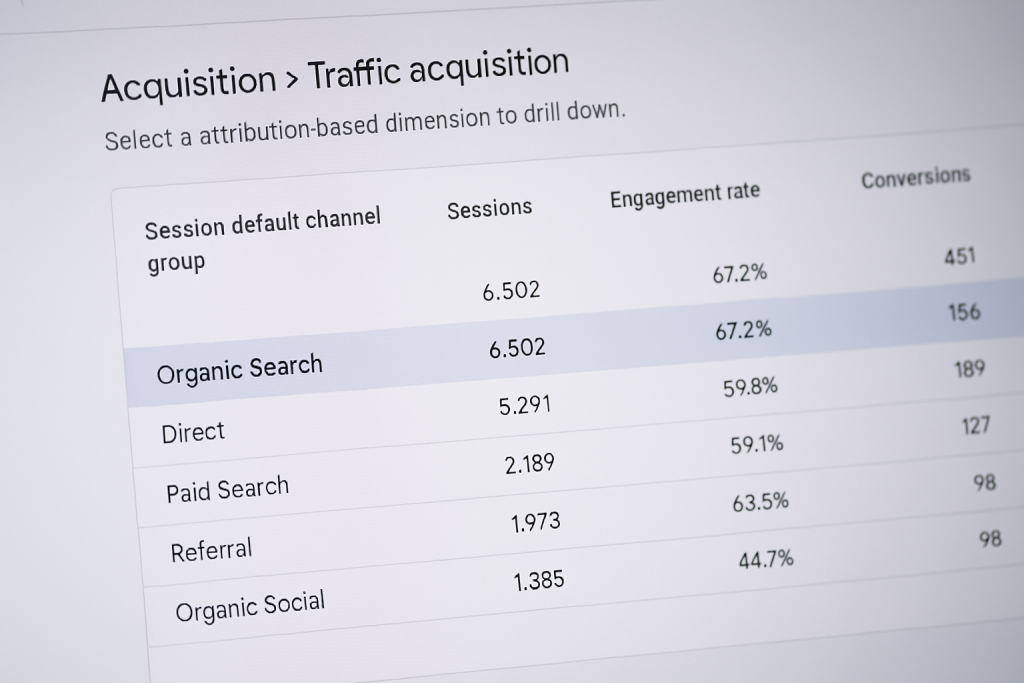
We keep things simple and results-focused. Our digital marketing affiliate program is designed for people who open doors to businesses with real marketing budgets and a mandate to grow. You don’t need to become a marketer; you bring the introduction, we do the work: strategy, analytics-led SEO, paid media, content, and continuous optimisation. You get rewarded for making the connection, and the client gains an agency that actually improves performance.
Because we work with mid-size and enterprise-level clients, the economics work in your favour. Our approach reduces churn and keeps clients longer, which means referral value compounds over time. If you prefer a digital marketing referral program that’s professional, transparent and built around measurable outcomes, this is it.
Who Should Join Our Digital Marketing Referral Program
Our program suits:
- Consultants and industry advisers who regularly meet marketing or growth decision-makers.
- Agency owners looking to resell or co-sell services where you don’t have capacity or specialism.
- Business development professionals and networkers with access to mid-market companies.
- Technology partners and SaaS vendors who want a partner to handle marketing for their customers.
As a partner reseller in our digital marketing agency’s affiliate program, you remain the introducer and trusted contact. Seek Marketing Partners handles qualification, proposals, delivery, and reporting. We keep you informed at every stage and provide co-branded materials so introductions convert.
How Our Digital Marketing Affiliate Program Works
We intentionally avoid complexity on this page. The process is straightforward and built to convert:
- Apply: tell us about your network and how you make introductions.
- Introduce: share a contact via a secure form or unique referral link.
- We qualify and propose: our team handles discovery and submits a clear proposal.
- Campaign delivery: we run the work end-to-end — SEO, PPC, content, analytics and optimisation.
- You’re rewarded: competitive, transparent commission paid on agreed terms.
If you want the exact terms, commission bands and payout schedule, contact us and we’ll share a concise partner pack. This landing page is designed to invite the right partners; it isn’t a contract or a full program disclosure.
What You’ll Get as a Digital Marketing Affiliate Partner and Reseller
- Clear partner onboarding and a dedicated partner manager.
- Co-branded sales collateral and sector-specific pitch decks to use when reaching out.
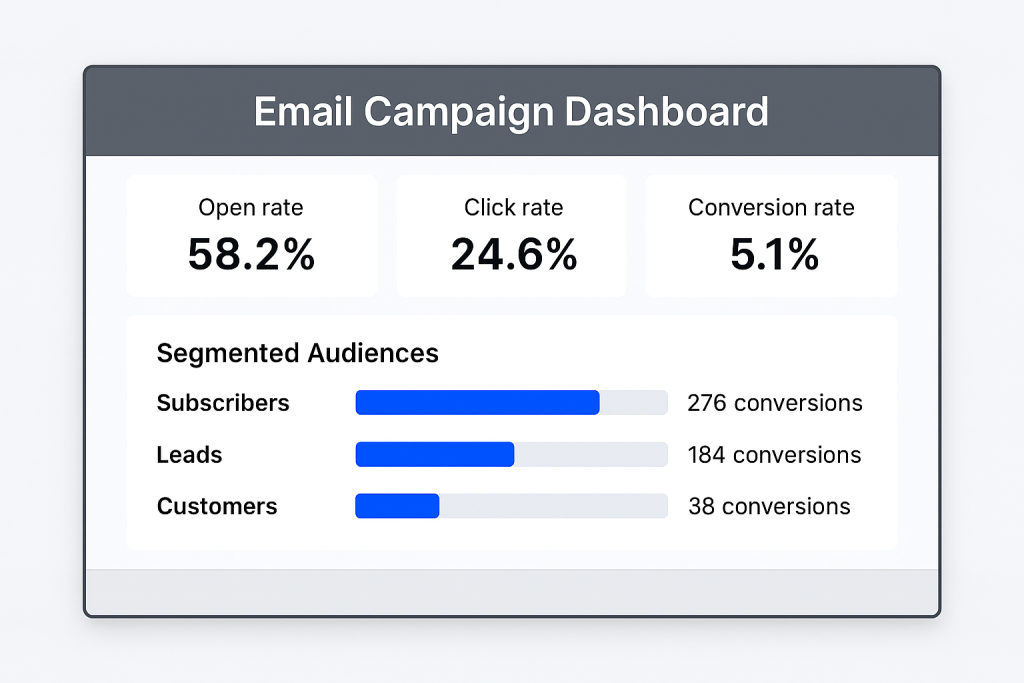
- Transparent tracking so you can see lead and pipeline status.
- Fast, reliable payments on conversion.
- Training on how to position our services for enterprise buyers.
We support partners and resellers of our digital marketing agency’s affiliate program with the tools they need to convert introductions into contracts without adding delivery work on their side.
Sectors Where Our Digital Marketing Affiliate Program Excels
Our sweet spot is mid-market and larger organisations in sectors where digital performance translates directly into revenue or leads:
- Technology & SaaS
- eCommerce & Retail
- Professional Services and B2B Lead Generation
- Finance & Insurance (commercial lines)
- Manufacturing & Industrial
- Hospitality & Travel
If your contacts sit in those areas, our digital marketing affiliate program is likely to be a particularly lucrative fit.
Why Recommend Seek Marketing Partners
We’re not promising magic; we promise grown-up marketing: analytics-driven strategy and specialised content that moves pipeline, not just vanity metrics. When you introduce a client, you’re recommending a partner that prioritises measurement, accountability, and long-term growth. That credibility makes your introductions easier to close and valuable to keep.
We also keep affiliate partner and reseller relationships professional: single-point partner managers, clear documentation, and an emphasis on mutual respect. If your reputation matters, you’ll find our approach reassuring.
Example Scenarios in Our Digital Marketing Affiliate Program
- A SaaS reseller introduces us to a customer who needs better trial-to-paid conversion. We handle the audits, experiments and rollout, and the reseller receives a partner payment.
- A consultant refers to a professional services firm needing lead generation and content. We deliver a multi-channel program, and the consultant is rewarded for the introduction.
For exact example calculations and commission models, contact us, and we’ll send the partner pack with everything you need to evaluate the opportunity.
Ready to Find Out More?
This page is intentionally concise; it’s a handshake, not a contract. Suppose you’re aligned with mid-size and larger organisations and want a credible, reliable way to monetise your network. Reach out, and we’ll send the partner pack and arrange a short conversation to confirm fit.
Contact us to learn more about the digital marketing affiliate program, tell us about the sectors you know and the types of contacts you can introduce. We’ll respond promptly and set out the next steps.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to be an agency to join?
No. You can be an individual consultant, an agency, or a technology partner. If you can make warm introductions to decision-makers, you qualify. Our program is designed to be inclusive, focusing on your ability to connect rather than your company type.
Do I have to do the delivery?
No. We deliver all marketing services. Your role is the introducer and trusted referrer. This means you can focus on building relationships while we handle the strategy, execution, and reporting.
Is the program public or invite-only?
We run an open application process but prioritise partners whose networks fit our mid-market/enterprise focus. Apply and we’ll talk you through fit and next steps. Our goal is to build a strong, aligned partner network that delivers real value to mid-size and larger organisations.
How do I get paid?
We agree on payment terms during onboarding. Payments are transparent and scheduled; we offer bank transfer or agreed payment methods. You can expect reliable, timely payments as part of our commitment to clear and fair partner relationships.
Can I resell services under my brand?
We offer partner models that include co-branded options and reseller pathways. We’ll discuss options in the partner conversation. This flexibility allows you to position our services in a way that best fits your business and client needs.